Performance
Overview
Sitefinity Cloud utilizes the following capabilities:
- CDN for the whole website
- Output cache
- Application warmup
- Auto-scaling
- External Blob storage
- Automated database performance optimization
CDN for the whole website
In Sitefinity Cloud, every request goes through a CDN, which then selectively caches the responses depending on the cache headers from the server. This includes the HTML markup of page requests. Caching pages on the CDN level can drastically boost website performance, not only in terms of speed, but also in terms of handling large load. This is achieved through the large global edge network covering all parts of the world.
Personalization and A/B testing
Sitefinity Cloud supports complex cases using CDN, such as A/B testing. Sitefinity Cloud automatically detects whether a page needs to be cached or not and provides the necessary cache-control header values to inform the CDN what to do. For example, pages that have active A/B tests will not be cached on the CDN. Pages that have fully personalized versions for the whole page will also be excluded from the CDN cache. Pages that have personalization per widget will have CDN cache, because the changes are applied client-side after the page is rendered.
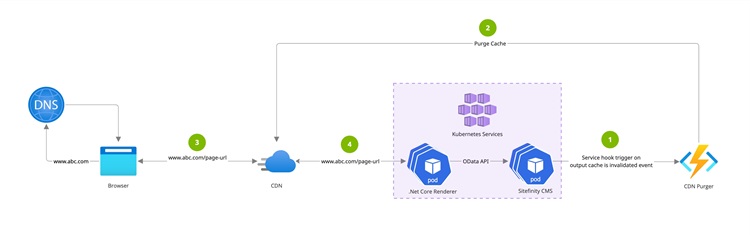
CDN caching with cache invalidation
In a classic setup, when using CDN, the CDN will continue serving the cached version of the content until the configured TTL (Time To Live) duration expires, after which the CDN cache is refreshed. This caching mechanism does not allow for long CDN cache durations, because website content can quickly become stale.
In Sitefinity Cloud, there is the following workflow configured to solve this problem:
- Output cache version of the page is updated or invalidated after which
IOutputCacheInvalidationEvent event is fired.
- Service hook is triggered for the
IOutputCacheInvalidationEvent event.
- CDN Purger function processes the service hook request payload and sends a CDN cache purge request.
- A request is sent to the CDN for the updated page.
- CDN sends a request to the Renderer application to retrieve the page, instead of serving it from cache.
The following diagram illustrates this workflow:
Output cache
The decoupled Renderer application uses the Sitefinity CMS API to get the necessary data to render any given page. Output cache is used in the Sitefinity CMS application for API responses that can be cached.
In Sitefinity Cloud setups where the Developer Extensions toggle is enabled (PaaS setup), and MVC pages are used instead of a decoupled Renderer, the system uses output cache for the page HTML.
Output cache warmup
Pages built with MVC (using legacy .NET) have worse performance than pages built with the decoupled Renderer approach using modern technologies like ASP.NET Core and Next.js. Output cache warmup is a powerful Sitefinity CMS feature used for MVC pages, which is configured with each Sitefinity Cloud PaaS setup where the Developer Extensions toggle is enabled.
When content editors make changes to content items that are displayed on one or more pages, the output cache for those pages is invalidated. This is done to ensure that the latest content is displayed to site visitors. The downside is that the first request for these pages is relatively slow, until the pages are cached again. Output cache warmup overcomes this slowdown. When using output cache, the website will request itself and cache the new version of the pages. This is done in the background and the performance of the first page request is hidden from site visitors - the old version of the page is displayed to site visitors, until the new version is cached. After the new version is cached, it is instantly displayed to the site visitors without decrease in performance.
The following diagram illustrates this workflow:
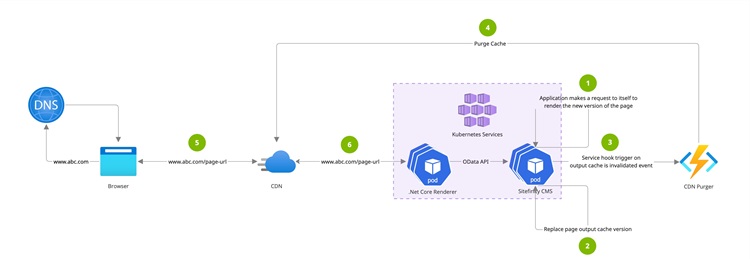
Application warmup
The warmup mechanism sends a set of requests to the application, which forces it to generate different levels of application cache, before it starts serving actual traffic.
Sitefinity Cloud uses the standard IIS warmup feature.
During deployment, the CI.CD pipeline gets the top 50 most viewed pages from the Application Insights and includes them in the <applicationInitialization> section of the web.config.
For more information, see Application warmup.
Auto-scaling
With load balancing and auto-scaling, Sitefinity Cloud intelligently distributes website visitors to the available web server nodes and scales out the number of nodes to accommodate traffic.
External Blob storage
Blob storage has the advantage of better scalability. When your Sitefinity Cloud database becomes too big, handling and restoring it may become time consuming. In this case, it is best to use external Blob storage for your media files.
Sitefinity Cloud uses Azure Blob Storage - it stores the binary blob data of Sitefinity Cloud library items on Azure Storage.
For more information, see Blob storage.
Automated database performance optimization
Database indexes are automatically rebuilt every 24 hours, depending on their fragmentation, for each environment.